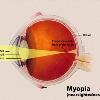
Myopia (lang-el??????, mu?pia, "nearsightedness"), is a refractive defect (Refractive error) of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus (focus (optics)) in front of the retina when accommodation (accommodation (eye)) is relaxed.
Those with myopia see (Visual perception) near objects clearly but far away objects appear blurred (Focus (optics)). With myopia, the eyeball is too long, or the cornea is too steep, so images are focused in the vitreous inside the eye rather than on the retina at the back of the eye. The opposite defect of myopia is hyperopia or "farsightedness" or "long-sightedness"?this is where the cornea is too flat or the eye is too small.
Eye care professionals most commonly correct myopia through the use of corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses. It may also be corrected by refractive surgery, but this does have many risks and side effects. The corrective lenses (lens (optics)) have a negative optical power (i.e. are concave) which compensates for the excessive positive diopters of the myopic eye.
Alternative ideas and methods of treatment exist, most notably the claim that myopia is caused by excessive near sight work.
Diseasesdb: 8729
Icd10: ICD10H521h49
Icd9: ICD9367.1
Meshid: D009216