Topics: Health Tags: Heart Failure View |
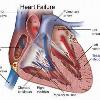
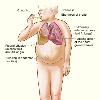
The illustration shows the major signs and symptoms of heart failure. Tags: Heart Failure View |
Topics: Health Tags: Heart Failure View |
|||||||||
Heart failure (HF) is generally defined as inability of the heart to supply sufficient blood flow to meet the bodys needs. It has various diagnostic criteria, and the term heart failure is often incorrectly used to describe other cardiac-related illnesses, such as myocardial infarction (heart attack) or cardiac arrest.
Common causes of heart failure include myocardial infarction (heart attacks) and other forms of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, valvular heart disease and cardiomyopathy. Heart failure can cause a large variety of symptoms such as shortness of breath (typically worse when lying flat, which is called orthopnea), coughing, ankle swelling and exercise intolerance. Heart failure is often undiagnosed due to a lack of a universally agreed definition and challenges in definitive diagnosis. Treatment commonly consists of lifestyle measures (such as decreased salt intake) and medications, and sometimes devices or even surgery.
Heart failure is a common, costly, disabling and potentially deadly condition. In developing countries, around 2% of adults suffer from heart failure, but in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6-10%. Mostly due to costs of hospitalization, it is associated with a high health expenditure; costs have been estimated to amount to 2% of the total budget of the National Health Service in the United Kingdom, and more than $35 billion in the United States. Heart failure is associated with significantly reduced physical and mental health, resulting in a markedly decreased quality of life. With the exception of heart failure caused by reversible conditions, the condition usually worsens with time. Although some patients survive many years, progressive disease is associated with an overall annual mortality rate of 10%.
Diseasesdb: 16209
Icd10: ICD10I50i30
Icd9: ICD9428.0
Medlineplus: 000158
Emedicinesubj: med
Emedicinetopic: 3552
Emedicine Mult: eMedicine2emerg108 eMedicine2radio189 eMedicine2med1367150 eMedicine2ped2636
Meshid: D006333