- » HIV/AIDS still a serious health problem: WHO
- » Kicking tobacco habit amongst HIV patients
- » Caribbean nations expect to receive $100 million grant from US government to fight AIDS
- » Days before Mother's Day, African, Canadian grandmothers gather in Swaziland to fight AIDS
- » HIV/Aids has become leading cause of death in women, warns UN
- » Anti-retroviral drugs may curb AIDS spread in 5yrs
- » Activists, medical community to Obama: More funding needed to fight AIDS in rural South
Tags: Aids View |
Topics: Health Tags: Aids View |
Topics: Health View |
|||||||||
Topics: Health Tags: Aids View |
Topics: Health Tags: Aids View |
Topics: Health Tags: Aids View |
|||||||||
Topics: Health Tags: Aids View |
Topics: Health Tags: Aids View |
AIDS: Acquired immune deficiency syndrome HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) CD4+: CD4+ T helper cells (T helper cell) CCR5: Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5) CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention WHO: World Health Organization PCP: Pneumocystis pneumonia TB: Tuberculosis MTCT: Mother-to-child transmission HAART: Highly active antiretroviral therapy (Antiretroviral drug) STI/STD: Sexually transmitted infection (Sexually transmitted disease)/disease
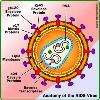
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (HIV).
This condition progressively reduces the effectiveness of the immune system and leaves individuals susceptible to opportunistic infections and tumors. HIV is transmitted (Transmission (medicine)) through direct contact of a mucous membrane or the bloodstream with a bodily fluid containing HIV, such as blood, semen, vaginal fluid, preseminal fluid, and breast milk.
This transmission can involve anal (anal sex), vaginal (vaginal sex) or oral (oral sex) sex (Sexual intercourse), blood transfusion, contaminated hypodermic needles, exchange between mother and baby during pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding or other exposure to one of the above bodily fluids.
AIDS is now a pandemic. In 2007, it was estimated that 33.2 million people lived with the disease worldwide, and that AIDS killed an estimated 2.1 million people, including 330,000 children. Over three-quarters of these deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa, retarding economic growth and destroying human capital.
Genetic research (Molecular phylogenetics) indicates that HIV originated in west-central Africa during the late nineteenth or early twentieth century. AIDS was first recognized by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 1981 and its cause, HIV, identified in the early 1980s.
Although treatments for AIDS and HIV can slow the course of the disease, there is currently no vaccine (HIV vaccine) or cure. Antiretroviral (antiretroviral drug) treatment reduces both the mortality (Mortality rate) and the morbidity of HIV infection, but these drugs are expensive and routine access to antiretroviral medication is not available in all countries. Due to the difficulty in treating HIV infection, preventing infection is a key aim in controlling the AIDS pandemic, with health organizations promoting safe sex and needle-exchange programmes in attempts to slow the spread of the virus.
Diseasesdb: 5938
Icd10: ICD10B24b20
Icd9: ICD9042
Medlineplus: 000594
Emedicinesubj: emerg
Emedicinetopic: 253
Meshid: D000163 style="float: right; clear:right; margin: 0 0 0.5em 1em; padding: 0.5em; background: #fffff4; border: solid #ddb; width: ; font-size:90%;"